The Source
The source is an ESG library with a great collection of articles, news, reports, research and videos on numerous topics related to ESG that has been curated and constantly updated by the EBI team.
Videos




ESG Business Institute 11 March 2025
The Influence of National Policy on ESG Standards Implementation







ESG Business Institute 21 October 2024
ESG Essentials: Building a Sustainable Future
Discover the core principles of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) frameworks and how they drive responsible business practices.

ESG Business Institute 16 August 2024
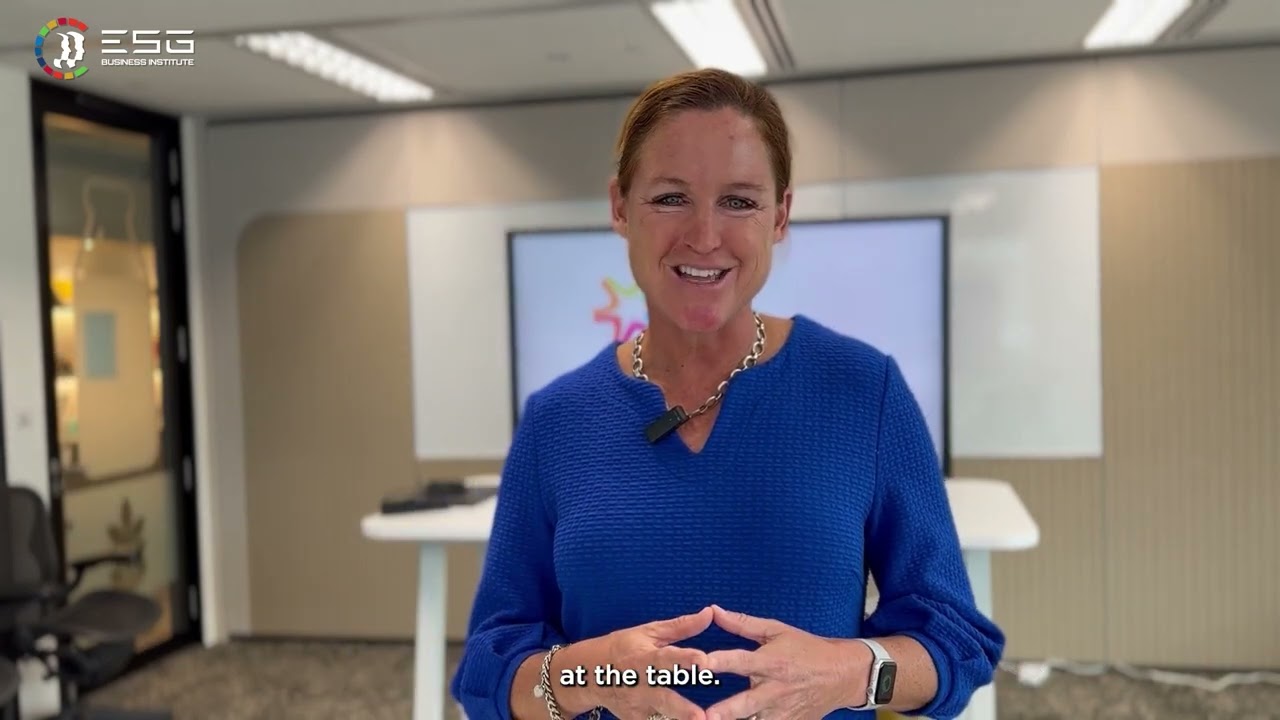
Women in Leadership: Inspiring Sustainability Champions
This episode of the The ESG Business Institute series features Corine Tap, President of FrieslandCampina in Asia, in a conversation with Genashtim's CEO, Thomas Ng. Tap discusses her commitment to sustainability and the essential role of women in leadership. She highlights the importance of creating inclusive environments that empower women to lead the ESG movement.

ESG Business Institute 16 August 2024
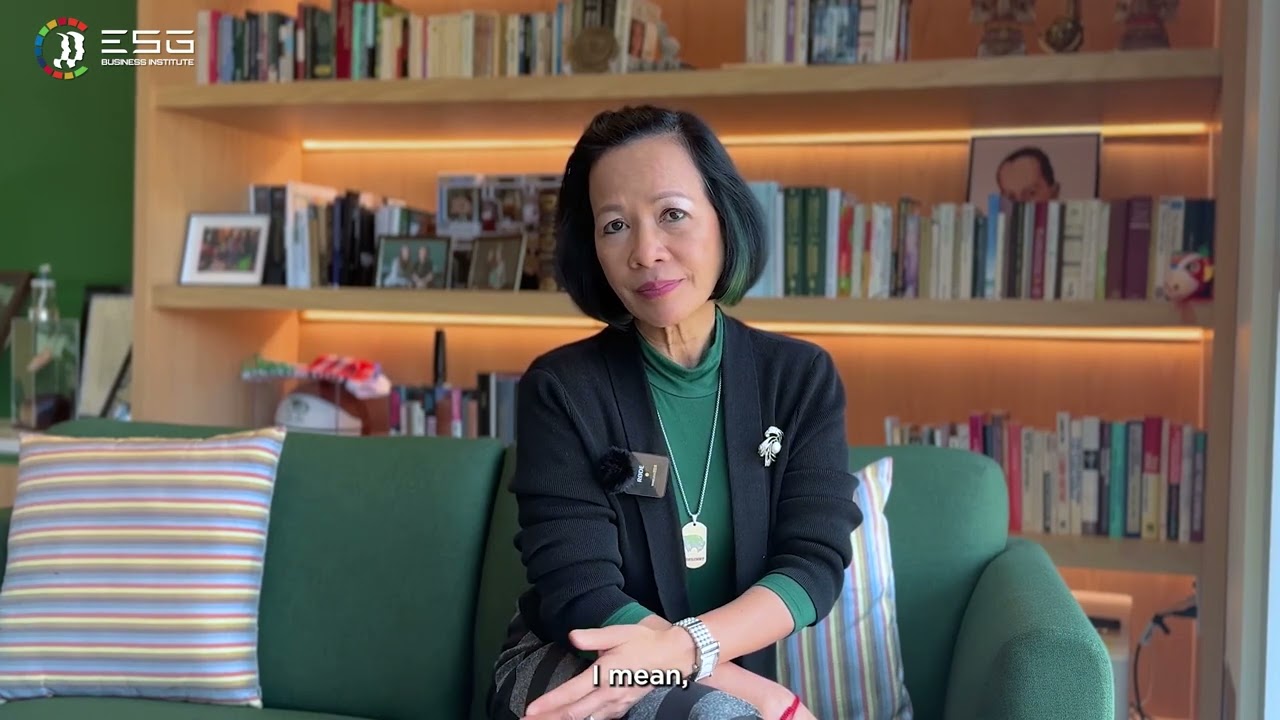
Woman in Leadership: Empowered Through Education
In celebration of International Women's Day, The ESG Business Institute proudly presents Dr. Astrid Tuminez, President of Utah Valley University, as she shares her inspiring journey from a humble background to becoming a global leader. Dr. Tuminez underscores the vital role of education and the empowering impact of scholarships in her path to success. Her story showcases the transformative power of education and the importance of diverse perspectives in leadership, aligning with The ESG Business Institute's commitment to promote inclusivity and sustainability in leadership.
ESG Business Institute 02 January 2024
Up Close with Chris Marquis
"Up Close with Chris Marquis" offers an insightful exploration into the future of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) practices. In this compelling series, host Chris Marquis, a renowned expert in sustainable business and corporate social responsibility, delves into the evolving landscape of ESG and its profound impact on businesses, investors, and society.

ESG Business Institute 14 March 2023
B Labs | The Hal Taussig 2022 Award | Yvon & Malinda Chouinard
B Labs | The Hal Taussig 2022 Award | Yvon & Malinda Chouinard
Latest News

ESG Business Institute 04 March 2026
Global ESG Regulatory Shifts: Streamlining and Expansion in 2026

ESG Business Institute 04 March 2026
ESG Finance in Action: Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners Acquires Ørsted's Onshore Renewables

ESG Business Institute 04 March 2026
Global Carbon Markets Under Scrutiny: Integrity and Volatility in 2026
NEWS
USA
ESG in the Crosshairs: How Politics Is Shaping the Future of Sustainability Introduction Once a ni...
🌍 Introduction: ESG’s Strategic Silence In the shifting terrain of corporate sustainabilit...
Climate reporting in the United States has entered a pivotal phase. In 2025, the ESG landscape is de...
The United States has witnessed significant policy changes under the Trump administration that w...
Is DEI Losing Its Spark, or Just Facing a Backlash? Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion ...
US DEI at a Turning Point The United States is witnessing seismic shifts in Diversity...
As Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting gains momentum, 2024 is expected to be a ...
The article "Clouds Emerge on Solar Horizon" explores the environmental downsides of solar power, fo...
Rajeev Peshawaria's article "3 Reasons Why ESG And COP Meetings Are Not Working" identifies three pr...
Key takeaways about B Corp brand awareness in 2023: Awareness Levels: Over one-third of adu...
The article "Sustainability and Abundance: A Futurist Explains How It Can Happen" discusses various ...
Cambridge professor, ESG Business Institute Board member, and author Christopher Marquis recently pe...
Investors at the WSJ Pro Sustainable Business Forum on Thursday said their interest in sustainabilit...
WASHINGTON—The White House is gearing up to inject a gusher of cash into hydrogen production, ...
More than two thirds of corporate boards lack a strong understanding of the ESG risks affecting thei...
The global energy system is governed by complex dynamics that play out over time across regions and ...
Lego, the world’s largest toy manufacturer, has built a reputation not only for the durability...
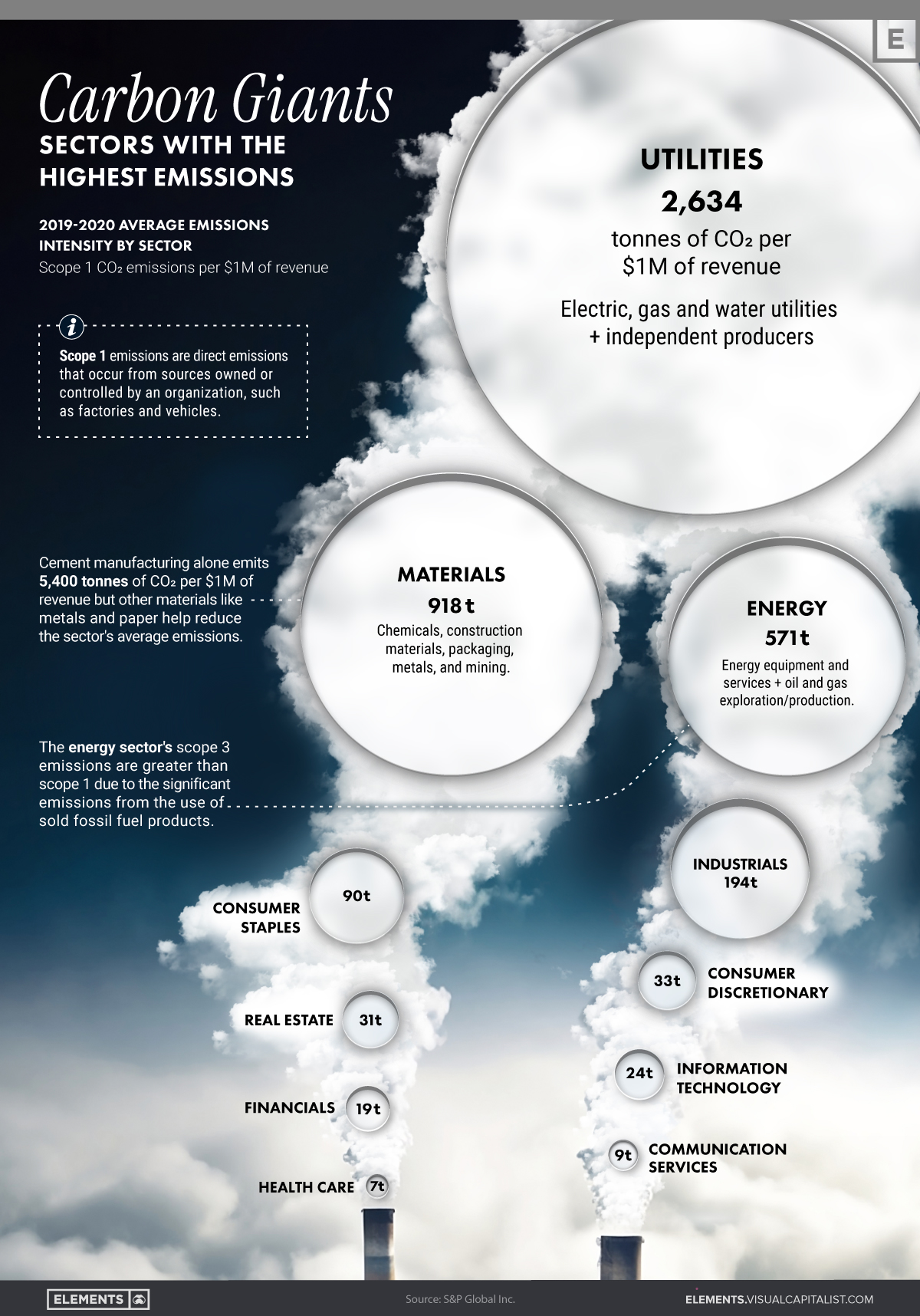
Ranked: The Most Carbon-Intensive Sectors in the World Ever wonder which sectors contribute the mos...
Europe
The Great Simplification Meets Bold Expansion December 2025 through February 2026 marks a turning p...
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY • Deal Value: €1.44 billion (~US...
Introduction: A Market at a Turning Point Global carbon markets were designed to put a price on p...
Executive summary — from ambition to accountability If 2024 was the year of ESG ambition and ...
Two of the world’s biggest climate polluters, China and the European Union, have made a joint ...
In today’s business world, sustainability is no longer just about carbon footprints or financi...
In a surprising turn of events, the European Union’s ambitious Corporate Sustainability Report...
Workplace violence and harassment are no longer just human rights concerns—they’re inv...
Imagine a future where sustainability data evolves beyond a corporate checkbox, transforming into ...
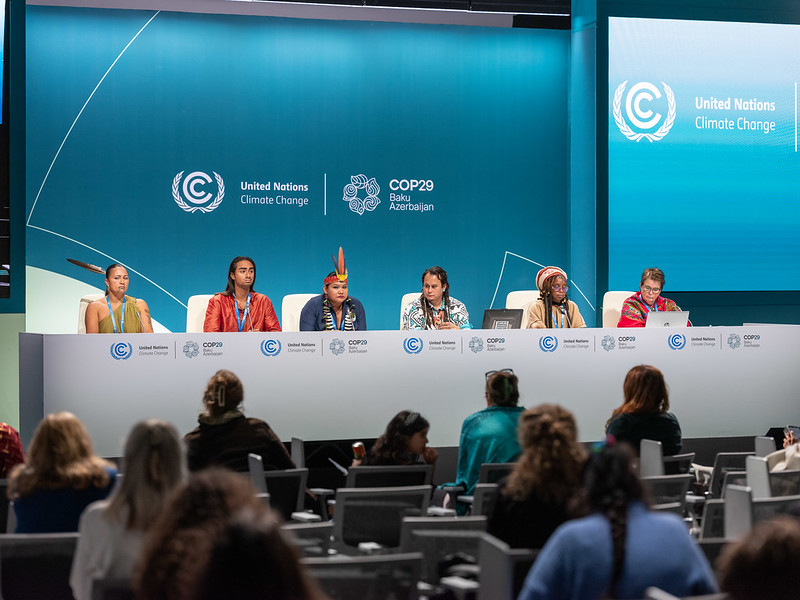
The 2024 United Nations Climate Change Conference, or COP29, held in Baku, Azerbaijan, marked anot...
The European Union (EU) is entering a transformative period in its approach to sustainability repo...
As climate regulations tighten, how prepared is your business for the EU’s Carbon Border Adj...
Growing concerns over plastic pollution and its harmful environmental impact have prompted inves...
Key points from PwC's Global CSRD Survey 2024: Widespread Awareness and Implementation: The...
The digital age has ushered in a transformative shift in the way companies ingest, store and analyze...
As the global business landscape continues to evolve, incorporating sustainability into reporting ...
ESG: From Process to Product Abstract ESG measurement, analysis, management, and communication is ...
ASIA PACIFIC
As ESG expectations rise globally, organizations continue to face a fundamental challenge: How ...
Introduction: Cities as ESG Frontlines By 2025, more than half of humanity lives in cities. Urban c...
Voluntary Carbon Markets (VCMs) are undergoing one of their most transformative periods yet. After y...
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations have entered a new era—one defined ...
Introduction: A New Roadmap for Decarbonization In September 2025, the Science Based Targets initia...
China’s Technology and Innovation in ESG: Lessons from BYD ESG: Two Different Stories In the...
Eco-friendly technologies are no longer a luxury. They’re a necessity amidst a more vola...
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, forward-thinking companies like Emapta’s...
When people hear “ESG”—Environmental, Social, and Governance—they often asso...
Carbon accounting has been regarded as a compliance burden—complex, costly, and confined to mu...
For decades, the global investment community has hesitated to fully embrace Africa, citing polit...
Australia’s financial regulator, ASIC, has released its new Regulatory Guide 280 (RG 280), o...
Ethiopia stands at a critical juncture as it confronts the multifaceted challenges posed by climat...
In an era where climate change poses significant risks, investing in impact-driven solutions is ...
Southeast Asia, a region home to over 650 million people, is at a critical juncture where ...
In our recent fireside chat, Karyanto Wibowo, Danone Indonesia's Sustainability Director, and Thom...
In a significant leap towards sustainability, the ASEAN region has unveiled Version 2 of its Taxonom...
An air of anxiety and anticipation percolated as the world watched COP28 unfold in the UAE in earl...
Study on "Advanced Grid-scale Energy Storage Technologies"...
KUALA LUMPUR: The response has been more positive from the corporate sector in integrating environme...
In our increasingly interconnected world, the telecommunications industryserves as the backbone of g...
JAKARTA, Sept 26 (Reuters) - Indonesian President Joko Widodo on Tuesday launched the country's firs...
Emerging global trends in mainstream transition to net-zero operations and positive social impact ...
PETALING JAYA: To accelerate environmental, social and governance (ESG) efforts among small and medi...
ESG compliance is becoming increasingly important in Singapore. Guided by the Singapore Green Plan 2...
Taiwan is actively promoting ESG compliance and sustainable business practices in response to the in...































.png)