Executive Summary
The past year has seen a marked rise in ESG disputes worldwide — from greenwashing claims to climate litigation against corporates and banks, and court interventions on fossil fuel approvals. Entering 2026, the trend is clear: fewer new rules, more enforcement and litigation.
Global companies now face mounting risks as regulators, competitors, and civil society actors challenge sustainability claims and practices. The message is unmistakable: weak ESG practices invite lawsuits, reputational damage, and investor flight.
What’s Hot in the Last 12 Weeks
- Litigation momentum: Legal bulletins highlight ongoing climate class actions (e.g., against a Dutch bank), dismissals of landmark claims (such as the RWE case in Germany), and court rulings requiring reconsideration of fossil project consents. The landscape is complex and case-by-case, with no single global precedent but a clear rise in enforcement.
- Market‑driven disputes: Beyond regulator actions, ESG controversies are increasingly initiated by shareholders and consumer groups. Reports note that investor coalitions in Europe have challenged overstated carbon‑neutral claims, while consumer protection agencies in North America have pursued misleading “eco‑friendly” product labels. These cases highlight that ESG disputes are now multi‑sourced - regulators, investors, and consumers alike are driving accountability (Crowe UK, Nov 2025; Morrison & Foerster, Jul 2025).
- Regional patterns: Dashboards tracking 2024–2025 filings show North America and Europe leading ESG litigation, while Asia-Pacific is rising, particularly around supply-chain and labor rights issues.
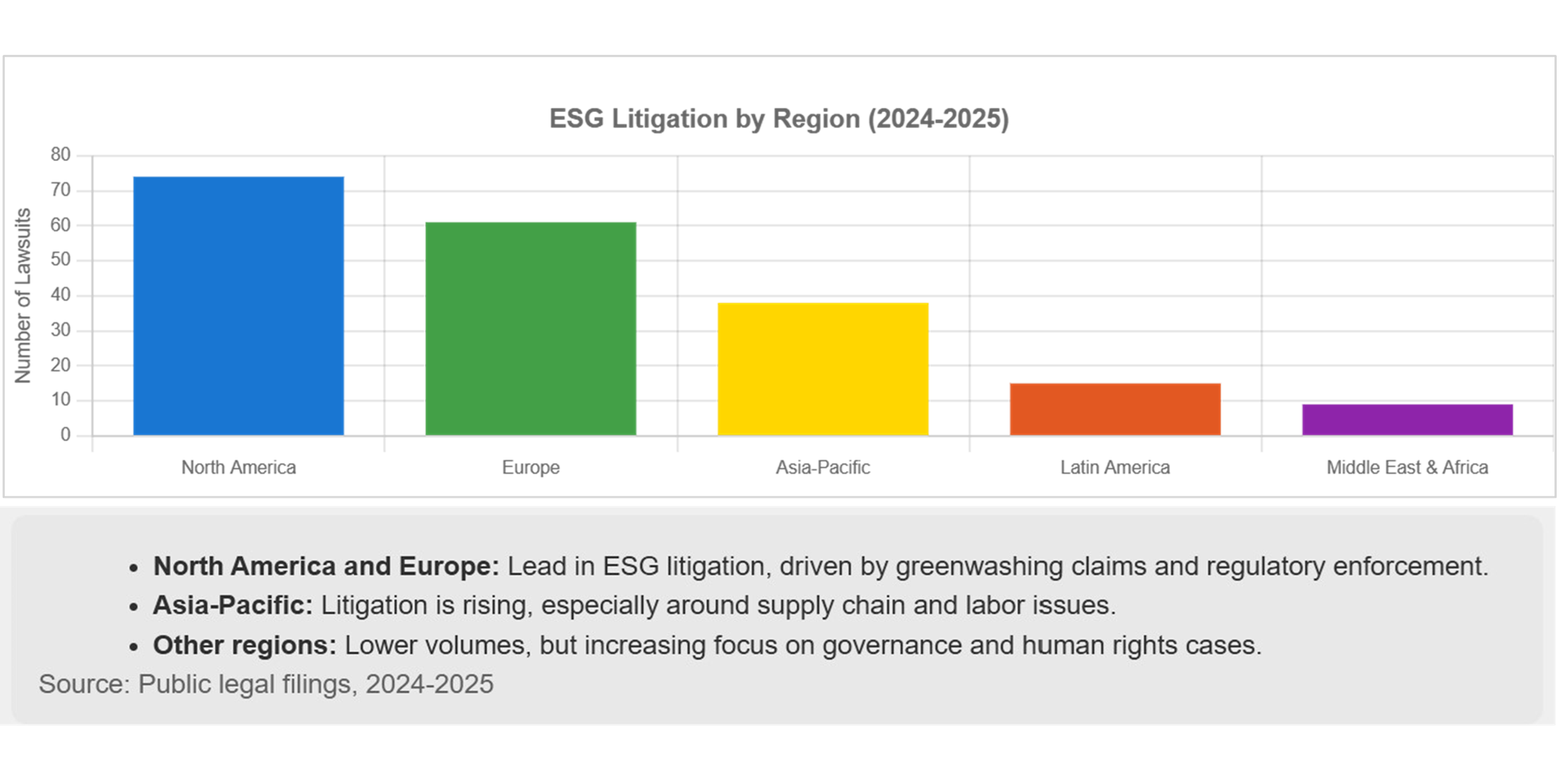
Global Controversy Types and Typical Triggers
| Category | Trigger | Risk Exposure |
|---|---|---|
| Greenwashing | Misleading sustainability claims, unverifiable metrics | Regulatory fines, competitor lawsuits |
| Climate Litigation | Emissions pathways, financing fossil projects | Court orders, reputational damage |
| Supply-Chain | Labor rights violations, traceability gaps | Import bans, investor divestment |
| Governance | Board oversight failures, whistleblower suppression | Lawsuits, valuation discount |
Case Studies — ESG Disputes in Action
In 2025, a Spanish renewable energy company faced a lawsuit from a competitor alleging misleading sustainability claims in its marketing materials.
- Trigger: The company advertised “100% green energy” without verifiable certification or third-party assurance.
- Outcome: The court ordered corrective disclosures and imposed fines, while reputational damage led to investor scepticism.
- Lesson: Greenwashing disputes are no longer confined to regulators — competitors are actively challenging claims to protect market credibility.
In late 2025, a coalition of NGOs filed a class action against a major bank for financing fossil fuel projects inconsistent with its public climate commitments.
- Trigger: The bank had pledged net-zero financing by 2050 but continued underwriting coal and oil expansion.
- Outcome: The case is ongoing, but early hearings have already forced the bank to disclose detailed climate risk assessments and reconsider fossil project approvals.
- Lesson: Climate litigation is expanding beyond corporates to include financial institutions, making financing decisions as vulnerable as operational ones.
Practical Moves for Global Companies
- Claims discipline: Tie every sustainability claim to verifiable, assured data. Avoid vague promises without interim milestones.
- Supply-chain controls: Implement traceability for high-risk inputs; publish grievance mechanisms and remediation outcomes.
- Governance rigor: Ensure board oversight of ESG, protect whistleblowers, and maintain evidence packs for audits and inquiries.
Technical Knowledge — Building Dispute-Resistant ESG
- Data assurance: Establish data lineage, owner sign-offs, and change logs; use independent verification for high-stakes metrics.
- Materiality mapping: Prioritize topics with legal exposure (greenwashing, labor rights, climate financing) and build controls first.
- Scenario planning: Run legal risk scenarios, prepare response playbooks for claims targeting products, financing, or suppliers.
Why This Matters Globally?
- Investor confidence: ESG controversies erode trust, leading to divestment and higher financing costs.
- Regulatory exposure: Courts are increasingly willing to intervene in fossil approvals and corporate climate claims.
- Competitive dynamics: ESG disputes are now market-driven, with competitors challenging each other’s credibility.
- Strategic resilience: Companies with robust ESG governance and verified data are better positioned to withstand scrutiny and litigation.

